Table of Contents
- What Are Gas Fees in Cryptocurrency?
- Why Do Gas Fees Exist?
- How Are Gas Fees Calculated?
- Gas Fees for Ethereum: What You Need to Know
- Factors That Influence Ethereum Gas Fees
- How to Check the Current Gas Fees
- How to Reduce Ethereum Gas Fees
- Gas Fees for Bitcoin vs. Ethereum
- Gas Fees for NFTs and Other Transactions
- Gas Fees on Trust Wallet, MetaMask, and Binance
- Future of Gas Fees: Will Ethereum Fees Go Down?
- To Recap
- FAQs
If you have ever traded cryptocurrency, you have likely encountered gas fees. These fees can be confusing, and their prices can change unpredictably.
In this guide, we will break down everything you need to know about gas fees in the simplest, most practical terms possible.
What Are Gas Fees in Cryptocurrency?
Gas fees in cryptocurrency are transaction costs paid to process and validate transactions on a blockchain network. In a manner of speaking, they are service charges for using the network.
When you send crypto like Ethereum (ETH) or Bitcoin (BTC), interact with smart contracts, or mint NFTs, miners or validators need computing power to confirm the transaction. Gas fees compensate them for this work.
Why Do Gas Fees Exist?
Gas fees exist because blockchain networks need a way to compensate the people who validate transactions and keep the network secure.
When you send cryptocurrency, swap tokens, or interact with smart contracts, your transaction must be processed by miners (on proof-of-work blockchains like Bitcoin) or validators (on proof-of-stake blockchains like Ethereum 2.0).
These miners and validators use computing power to verify transactions, add them to the blockchain, and ensure everything runs smoothly. The gas fee for Ethereum, for example, is a charge that users pay to these validators for processing their transactions.
Without gas fees, there would be no incentive for miners or validators to confirm transactions, which could lead to network congestion and security risks.
Gas fees also prevent spam attacks on the network by making it expensive to flood the blockchain with fake transactions. While gas fees may seem like an extra cost, they serve a crucial purpose in keeping Ethereum and other blockchains efficient and secure.
How Are Gas Fees Calculated?
1. Understanding Gas Price (Gwei):
Gas fees on Ethereum are measured in a unit called Gwei, which is a smaller unit of Ether (ETH). 1 Gwei = 0.000000001 ETH. The gas price is the amount of Gwei you are willing to pay per unit of gas to get your transaction processed. If you offer a higher gas price, miners or validators will prioritise your transaction.
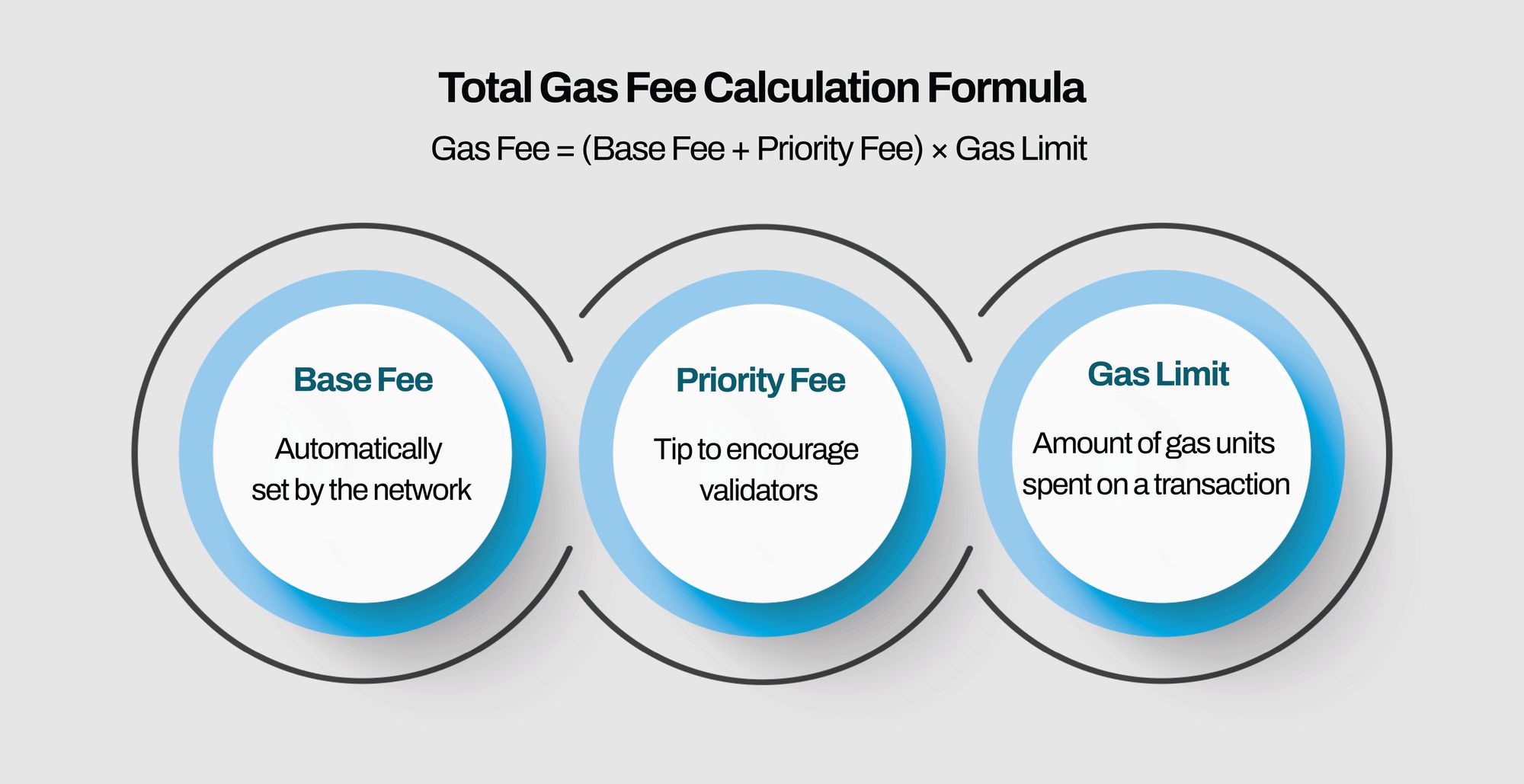
2. Base Fee (Mandatory Network Fee):
Every Ethereum transaction requires a base fee, which is set automatically by the network. This base fee changes depending on how busy the Ethereum network is. When the network is congested, the base fee increases, making transactions more expensive.
3. Priority Fee (Tip to Speed Up Transactions):
You can add a priority fee (also called a "tip") to encourage validators to process your transaction faster. If you don’t add a tip, your transaction might take longer to be confirmed.
4. Gas Limit (Maximum Gas You Allow for a Transaction):
The gas limit is the maximum amount of gas units you are willing to spend on a transaction. Simple transactions like sending ETH usually require 21,000 gas units, while more complex transactions like swapping tokens or minting NFTs can use hundreds of thousands of gas units.
5. Total Gas Fee Calculation Formula:
The total gas fee you pay is calculated as:
Gas Fee = (Base Fee + Priority Fee) × Gas Limit
For example, if the base fee is 30 Gwei, the priority fee is 10 Gwei, and the gas limit is 21,000, then:
Gas Fee = (30 + 10) × 21,000 = 840,000 Gwei (or 0.00084 ETH)
If 1 ETH = $3,000, the gas fee in USD would be:
0.00084 × 3,000 = $2.52
6. Network Congestion Affects Gas Fees:
If more people are using Ethereum at the same time, gas fees increase. This is why gas fees for today may be different from tomorrow.
7. Using a Gas Fee Estimator:
You can check gas fees before making a transaction using a gas fee estimator like Etherscan’s Gas Tracker or the gas fee estimator in MetaMask.
8. Choosing the Right Time to Pay Lower Fees:
Gas fees are usually lower when the network is less busy. The lowest gas fees for ETH are often found early in the morning (UTC time) or during weekends.
Gas Fees for Ethereum: What You Need to Know
Gas fees for Ethereum are the transaction costs required to process and validate operations on the Ethereum blockchain.
These fees are measured in gwei (1 gwei = 0.000000001 ETH) and fluctuate based on network demand.
When the Ethereum network is congested, gas fees rise because more people are trying to complete transactions simultaneously. On the other hand, during off-peak periods, fees can drop significantly.
The average gas fee on Ethereum varies daily, but in 2024, it ranged between 5 gwei and 150 gwei, depending on network activity.
For example, sending ETH from one wallet to another may cost between $1 and $10, while more complex transactions like swapping tokens or minting NFTs can cost $50 or more.
To estimate how much the gas fee for Ethereum is, traders use tools like the Ethereum Gas Fee Estimator on platforms like Etherscan.
If you’re wondering how to avoid Ethereum gas fees or get the lowest gas fees for ETH, the best approach is to transact during low-traffic hours, such as early mornings or weekends.
Also, some crypto wallets, like Trust Wallet and MetaMask, offer gas fee settings, allowing users to adjust fees based on priority.
While Ethereum’s high gas fees have been a concern, upgrades like Ethereum 2.0 and Layer 2 solutions (e.g., Arbitrum and Optimism) aim to reduce costs, making transactions more affordable.
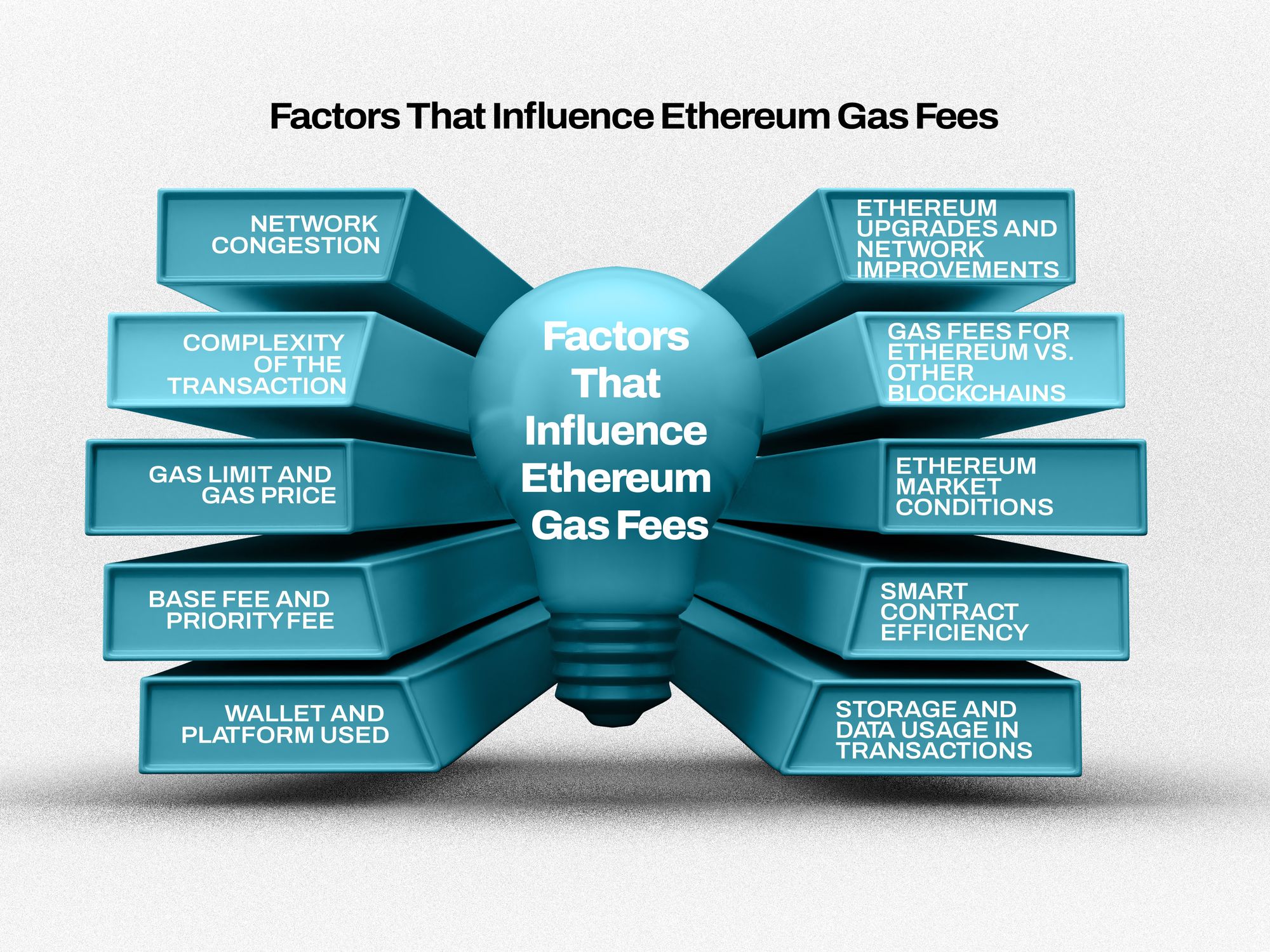
Factors That Influence Ethereum Gas Fees
1. Network Congestion:
Ethereum operates on a blockchain network where transactions compete for space in each block. When many people are making transactions at the same time, the demand for block space increases, leading to higher gas fees.
This is similar to rush hour traffic—when more people are on the road, it takes longer and costs more to get to your destination. The average gas fee on Ethereum can spike during peak periods and drop when activity is lower. If you want the lowest gas fees for ETH, consider transacting during off-peak hours.
2. Complexity of the Transaction:
Not all Ethereum transactions require the same amount of gas. Sending ETH from one wallet to another costs less gas than executing a smart contract or minting an NFT. This is because complex transactions require more computational power.
For example, the Ethereum gas fees for minting an NFT are usually higher than a simple ETH transfer. If you want to avoid Ethereum gas fees, choose transactions that require less computational effort.
3. Gas Limit and Gas Price:
Every Ethereum transaction has two main components: the gas limit and the gas price. The gas limit is the maximum amount of gas you are willing to spend on a transaction, while the gas price is how much you are willing to pay per unit of gas.
If you set a low gas price, your transaction may take longer to process or fail. A gas fee estimator ETH tool can help you determine the best gas price at any given time.
4. Base Fee and Priority Fee (Tips):
Ethereum uses a fee structure that includes a base fee (which is burned) and a priority fee (tip) that goes to miners or validators. The base fee adjusts automatically depending on network demand.
If you want your transaction to be processed faster, you can add a higher tip, increasing the gas fee Ethereum swap cost.
5. Wallet and Platform Used:
Different wallets and platforms have varying gas fee structures. For example, the gas fee on Trust Wallet might be slightly different from the gas fee Ethereum Metamask charges because each platform has its own way of calculating fees.
Some exchanges and wallets may offer gas fee ETH refund promotions or use batching methods to lower costs.
6. Ethereum Upgrades and Network Improvements:
Ethereum is constantly evolving, and upgrades like Ethereum 2.0 aim to reduce gas fees. In the past, gas fees were higher due to the proof-of-work system, but with Ethereum’s transition to proof-of-stake, ETH gas fees in USD may become more stable.
However, major updates can also temporarily cause fluctuations in the Ethereum gas fees price.
7. Gas Fees for Ethereum vs. Other Blockchains:
Ethereum’s gas fees are often compared to those of other blockchains like Bitcoin and Solana. ETH gas fees can be quite different from BTC because Bitcoin operates on a different network that doesn’t use gas fees in the same way.
Similarly, Ethereum vs. Solana gas fees vary because Solana has a different transaction processing system.
8. Ethereum Market Conditions:
Gas fees are also influenced by the overall state of the Ethereum market. If ETH prices rise, transaction fees (which are calculated in ETH) may also increase when converted to fiat currency.
The comparison of the ETH-USDT gas fee shows that fees fluctuate based on Ethereum’s price movements.
9. Smart Contract Efficiency:
Some smart contracts are written in a way that makes them inefficient, requiring more gas to execute. Developers can optimise contracts to reduce costs, but if a contract is poorly written, the gas fee for sending ETH through it will be higher.
If you are frequently interacting with decentralised apps (dApps), check if they offer gas-efficient transactions.
10. Storage and Data Usage in Transactions:
Transactions that involve storing large amounts of data on the blockchain require more gas. For example, saving an image on the Ethereum blockchain costs more than a simple ETH transfer.
Platforms like OpenSea show the gas fee Ethereum Opensea chart to help users understand costs related to NFT transactions.
How to Check the Current Gas Fees
1. Use a Gas Fee Estimator:
Many platforms provide real-time gas fee estimators for Ethereum transactions. Websites like Etherscan Gas Tracker and ETH Gas Station show the current gas fee in gwei (the smallest unit of ETH).
These platforms also offer estimated fees for slow, average, and fast transactions, helping you decide when to process your transaction for the lowest cost.
2. Check Your Crypto Wallet:
Most crypto wallets, like Metamask, Trust Wallet, and Coinbase Wallet, display estimated gas fees before you confirm a transaction.
If you are using Metamask, you can check the “Advanced Gas Controls” section to manually set gas fees based on network conditions. Trust Wallet also shows gas fees when sending ETH, swapping tokens, or minting NFTs.
3. Look at Blockchain Explorers:
Blockchain explorers like Etherscan and BscScan provide updated gas fee charts. If you want to check Ethereum gas fees, simply search for the latest block transactions to see the gas fees paid by recent users. This helps you understand the typical fees for sending ETH or swapping tokens.
4. Use Crypto Exchange Platforms:
Some crypto exchanges, like Obiex, offer gas fee calculators when you withdraw or swap Ethereum-based tokens. If you want to find the lowest gas fees for ETH, compare fees across different exchanges before making a transaction.
5. Follow Gas Fee Alerts on Telegram and Twitter:
Some Telegram bots and Twitter accounts post live gas fee updates. For example, accounts like @EthGasAlerts notify traders when Ethereum gas fees for minting NFTs or other transactions are low. This is useful if you want to time your transaction when fees are cheaper.
6. Use Gas Fee Prediction Tools:
Some tools like Blocknative Gas Estimator predict gas fee changes by analysing network activity. If you’re wondering when to get the lowest gas fees for ETH, these tools can help you schedule transactions during off-peak hours to avoid Ethereum gas fees.
How to Reduce Ethereum Gas Fees
1. Use the Ethereum Network During Off-Peak Hours:
The best way to get the lowest gas fees for ETH is to transact when fewer people are using the network. Typically, Ethereum gas fees are lower on weekends and during late-night hours (UTC). Using a gas fee estimator ETH tool like Etherscan can help you find the best time before making a transaction.
2. Use Layer 2 Solutions:
Layer 2 solutions like Optimism, Arbitrum, and zkSync help reduce gas fees by processing transactions off the Ethereum mainnet. These networks are built on Ethereum but use cheaper transaction methods, significantly lowering gas fees for Ethereum swaps, transfers, and NFT minting.
3. Adjust Gas Fees Manually on Wallets:
Many wallets, including MetaMask and Trust Wallet, allow users to adjust gas fees manually. If you are not in a hurry, setting a lower gas price can help you avoid Ethereum gas fees when they are too high. However, be careful—setting the gas fee too low may delay your transaction or cause it to fail.
4. Use Gas Tokens (If Available):
Gas tokens like Chi and GST2 allow users to pre-purchase gas at lower prices and use it later when fees are high. This method is not as common today but can still be useful in specific cases, especially for frequent Ethereum users.
5. Choose Wallets and Platforms with Low Fees:
Some wallets and platforms offer cheaper Ethereum gas fees compared to others. If you are transferring ETH or swapping tokens, checking different platforms can help you find the cheapest Ethereum gas fees available at the moment.
6. Use the Right Type of Transaction:
Ethereum allows users to select different transaction types, such as EIP-1559 transactions (which use a base fee and a tip). Choosing the right type of transaction based on current network conditions can help reduce costs and improve efficiency.
7. Bridge to Cheaper Blockchains:
Some blockchains, like Polygon, Solana, and Binance Smart Chain (BSC), have lower transaction fees compared to Ethereum. Using a bridge to move assets between Ethereum and these networks can help reduce gas costs significantly.
8. Use Batched Transactions:
If you need to send multiple transactions, some platforms allow you to batch them into a single transaction, reducing overall gas fees. This is useful for businesses, NFT creators, and users making frequent transactions.
9. Monitor Gas Fees Before Transacting:
Always check the gas fee before making a transaction. Websites like Etherscan Gas Tracker and GasNow provide real-time estimates, helping you decide the best time to send ETH and reduce costs.
10. Wait for Ethereum Upgrades:
Ethereum is constantly evolving. Future upgrades like Ethereum 2.0 aim to reduce gas fees by shifting from Proof of Work (PoW) to Proof of Stake (PoS). Keeping up with network improvements can help you plan transactions at the right time for lower costs.
Gas Fees for Bitcoin vs. Ethereum
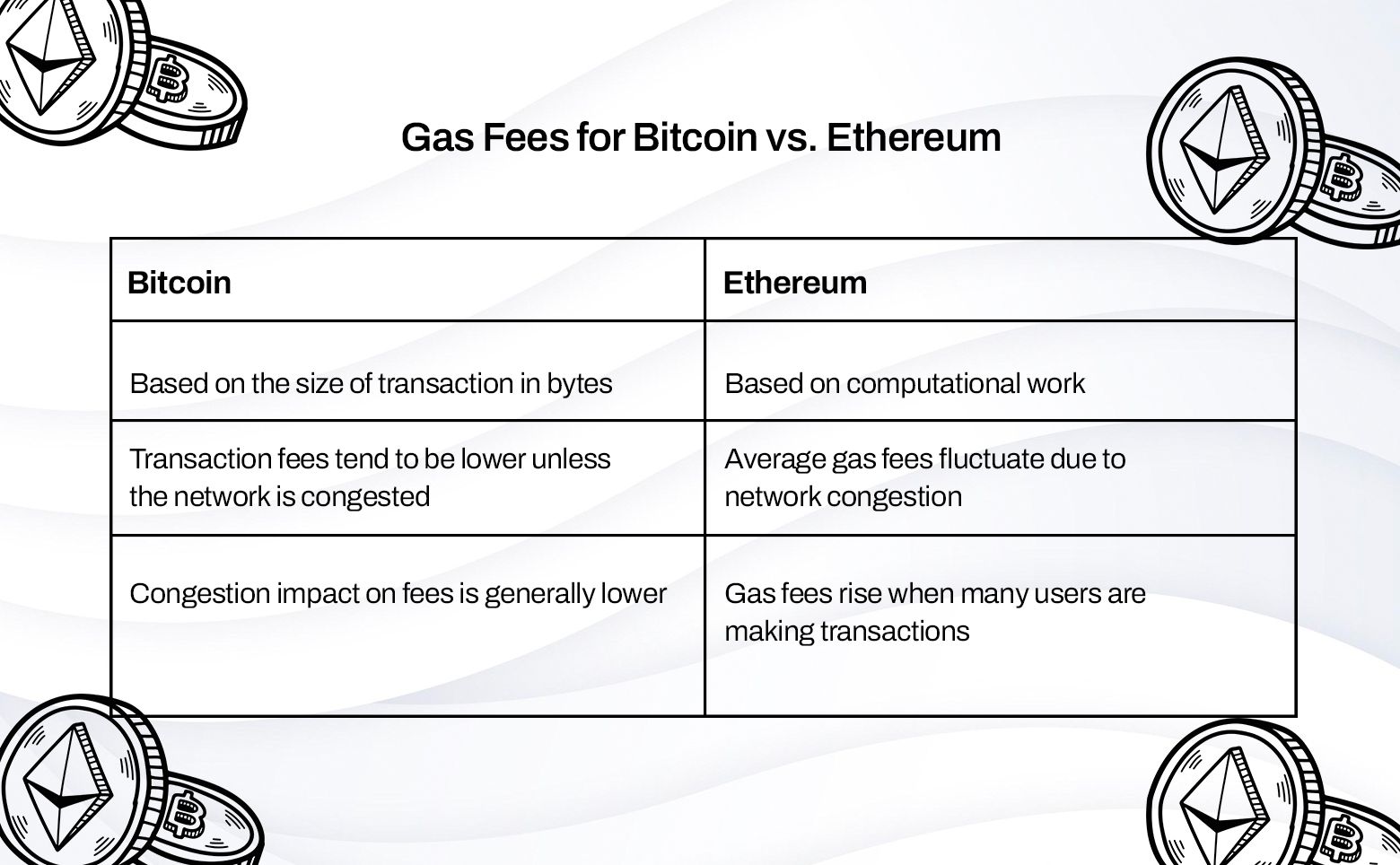
1. How Fees Are Calculated:
Bitcoin transaction fees are based on the size of the transaction in bytes, not its value. This means that a transaction with more inputs and outputs will cost more, even if the amount of BTC being sent is small.
Ethereum gas fees, on the other hand, are based on computational work. The more complex a transaction (such as interacting with a smart contract), the more gas it requires, increasing the total gas fee for Ethereum transactions.
2. Average Cost of Transactions:
The average gas fee on Ethereum fluctuates due to network congestion. As of 2024, Ethereum gas fees can range between $1 and $50, depending on network activity. However, for complex transactions like swapping tokens or minting NFTs, fees can go much higher.
On the other hand, Bitcoin transaction fees tend to be lower in comparison, averaging between $1 and $5, unless the network is congested.
3. Impact of Network Congestion:
Ethereum gas fees rise when many users are making transactions simultaneously. This happens because Ethereum uses a bidding system where users pay more to have their transactions processed faster.
Bitcoin also experiences congestion, but its impact on fees is generally lower because transaction fees are set based on size, not competition.
4. Different Use Cases Affect Fees:
Bitcoin transactions are mainly for peer-to-peer payments, meaning fees remain relatively stable.
Ethereum, however, supports smart contracts, NFTs, and DeFi transactions, all of which require more computation, leading to higher gas fees.
This makes the purpose of gas fees in Ethereum transactions different from those in Bitcoin.
5. Methods to Reduce Fees:
Ethereum users can reduce gas fees by making transactions during low gas fee times, typically during weekends or late at night. They can also use layer-2 solutions like Arbitrum and Optimism to avoid Ethereum gas fees.
Bitcoin users can save on fees by using SegWit and batching transactions.
6. Refunds and Estimations:
Ethereum users can check gas fee estimators for ETH to plan transactions at the cheapest Ethereum gas fees. Some wallets also provide Ethereum gas fee calculators to help users decide when to transact.
Bitcoin doesn’t have a gas refund system, but users can use fee estimators to check gas fees ETH vs BTC before making transactions.
7. Future Outlook for Fees:
Ethereum’s transition to Ethereum 2.0 and rollups like zkSync aim to bring lower gas fees for ETH transactions.
In contrast, Bitcoin’s Lightning Network is being developed to make BTC transactions faster and cheaper. If successful, both networks could see reduced transaction costs in the coming years.
Gas Fees for NFTs and Other Transactions
1. Gas Fees for Minting NFTs:
NFT minting is the process of creating a unique digital asset on the blockchain. Since this involves executing smart contracts, gas fees can be high.
The average Ethereum gas fee for minting an NFT can range from $10 to $100 or more, depending on network activity. Platforms like OpenSea and Rarible often experience higher fees due to demand spikes.
To reduce costs, users should mint NFTs when network activity is low.
2. Gas Fees for Buying and Selling NFTs:
Buying and selling NFTs also require gas fees, particularly when using decentralised marketplaces like OpenSea, Foundation, and LooksRare. Gas fees cover smart contract execution and transaction validation.
The current gas fee for Ethereum varies but typically ranges between $5 to $50 per transaction. Users can save on fees by trading during off-peak hours.
3. Gas Fees for Sending ETH and Tokens:
Transferring ETH or ERC-20 tokens between wallets incurs a gas fee. The gas fee for sending ETH depends on transaction speed preferences.
A standard transfer may cost $1 to $10, while a faster transaction may require higher fees. Tools like an ETH gas fee estimator help users calculate costs in advance.
4. Gas Fees for Swapping Tokens:
Swapping tokens on decentralised exchanges (DEXs) like Uniswap and PancakeSwap involves interacting with liquidity pools, which increases gas fees.
A simple swap can cost anywhere from $5 to $30, while complex trades with multiple steps can be higher. Using layer-2 solutions like Arbitrum and Optimism can help reduce costs.
5. Gas Fees for Staking and Yield Farming:
Staking and yield farming require gas fees for depositing and withdrawing funds. The gas fee for staking can range from $10 to $50, depending on the platform and network congestion.
Ethereum users looking for lower fees often use alternative blockchains like Solana and Binance Smart Chain (BSC).
Gas Fees on Trust Wallet, MetaMask, and Binance
Here's a breakdown of how gas fees work on each platform and what you need to know about them:
1. Gas Fee on Trust Wallet:
Trust Wallet is a popular mobile wallet for managing various cryptocurrencies, including Ethereum.
When you make a transaction or interact with a decentralised application (dApp), you'll need to pay a gas fee to process the action on the Ethereum blockchain.
The fee is determined by the network’s demand and the complexity of the transaction.
Trust Wallet doesn't set the fee directly, but it allows users to adjust the gas price when making a transaction.
It's important to check the gas fee estimator in Trust Wallet before sending ETH or performing any action to avoid overpaying or delays.
2. Gas Fee on MetaMask:
MetaMask is another widely used Ethereum wallet, especially for interacting with dApps.
The gas fee on MetaMask is similar to Trust Wallet, as it's determined by the Ethereum network.
MetaMask provides an option to adjust the gas fee based on how fast you want the transaction to be processed.
If you choose a higher fee, your transaction will be processed quicker, but if you select a lower fee, it may take longer to confirm.
It's recommended to use the gas fee estimator tool available on MetaMask to help determine the best fee for your transaction.
3. Gas Fee on Binance:
Binance is a cryptocurrency exchange that allows users to buy, sell, and store ETH and other cryptocurrencies.
Binance charges gas fees when users transfer Ethereum to and from the exchange or when making any other transactions within their wallet.
While Binance’s gas fees are often lower than those on Ethereum’s native network, they are still subject to the same market forces, meaning they can fluctuate depending on network congestion.
If you're using Binance to perform Ethereum swaps or send ETH, the gas fees can vary. Always check the current gas fee estimator on Binance before making large transactions, especially when transferring ETH to your personal wallet or dApp.
Future of Gas Fees: Will Ethereum Fees Go Down?
Ethereum gas fees have been a topic of concern for many crypto traders, especially as they can vary greatly depending on the network’s activity. The question of whether Ethereum gas fees will go down is something that many traders and investors are hoping to get an answer to.
Right now, gas fees for Ethereum are often high, particularly when there is a lot of activity on the network, such as during NFT minting or major token swaps. However, there are ongoing efforts within the Ethereum community to reduce these fees.
One of the most significant changes is Ethereum 2.0, which is designed to improve scalability and transaction speed by transitioning from a proof-of-work (PoW) model to proof-of-stake (PoS).
This shift aims to make Ethereum more efficient, reducing congestion on the network and lowering gas fees.
Additionally, layer 2 solutions are gaining popularity as they help process transactions off the main Ethereum blockchain, which also helps reduce the strain on the network.
With these improvements, the hope is that gas fees for Ethereum transactions—whether you’re sending ETH, swapping tokens, or even minting NFTs—will gradually decrease.
That said, the timeline for significant reductions is uncertain, and gas fees can still fluctuate depending on demand. As Ethereum continues to evolve, traders and users can expect lower gas fees, but the extent and speed of this decrease will depend on the success of these upgrades.
To Recap
- Gas Fees are transaction costs paid to miners or validators to process and validate transactions on a blockchain.
- Gas fees compensate miners/validators for securing the network and prevent spam attacks.
- Gas fees consist of base fees, priority fees, and gas limits, and depend on network congestion.
- Ethereum Gas Fees vary based on network activity and can range from $1 to $50 or more, depending on transaction complexity.
- Factors influencing gas fees include network congestion, transaction complexity, and the wallet/platform used, which all impact gas fees.
- Use gas fee estimators like Etherscan or your wallet’s gas fee tracker to check current gas fees.
- Reduce fees by transacting during off-peak hours, using Layer 2 solutions, adjusting gas fees, or selecting platforms with lower fees.
- Ethereum's gas fees differ from Bitcoin and Solana due to different transaction processing methods.
- Ethereum 2.0 and Layer 2 solutions aim to reduce gas fees over time.
- NFTs and Smart Contract transactions often require more gas due to higher computational demand.
- Ethereum upgrades and Layer 2 solutions may lead to reduced gas fees in the future.
FAQs
Q1. What is gas fee in cryptocurrency?
It is the transaction cost paid to process and confirm transactions on the blockchain.
Q2. What does gas fee mean in crypto?
It refers to the small fee required to execute transactions on a blockchain network.
Q3. How much is gas fee for Ethereum today?
It varies but can range from $5 to $50, depending on network congestion.
Q4. Why does Ethereum have gas fees?
Gas fees help pay for computational power and prevent spam transactions.
Q5. How can I avoid high Ethereum gas fees?
Use layer-2 solutions, time transactions during low network activity, or use fee optimisation tools.
Q6. How do I check the gas fee for sending ETH?
You can check gas fees using tools like Etherscan, Gas Now, or your crypto wallet.
Q7. Will Ethereum gas fees go down?
Ethereum 2.0 and layer-2 solutions are expected to reduce gas fees significantly.
Q8. What is the gas fee for Ethereum on Trust Wallet?
It varies depending on network congestion but is displayed before confirming a transaction.
Q9. When is the best time to pay the lowest Ethereum gas fees?
Late at night or early in the morning when network traffic is low.
Q10. What is the difference between Ethereum and Bitcoin gas fees?
Ethereum fees depend on gas limits and prices, while Bitcoin fees follow a fee-per-byte model.
Disclaimer: This article was written to provide guidance and understanding. It is not an exhaustive article and should not be taken as financial advice. Obiex will not be held liable for your investment decisions.

