Table of Contents
- What Is a Crypto Partner’s KYC Stack?
- When Should You Audit a KYC Stack?
- What You Need Before Auditing
- Key Components to Audit in a Crypto KYC Stack
- Questions You Should Ask Your Crypto Partner (Checklist)
- Red Flags to Watch Out For
- What a Strong KYC Stack Looks Like (Obiex’s Approach)
- How Obiex Helps You Integrate with Confidence
- To Recap
- FAQs
If you're a fintech operator, product manager, or CTO exploring crypto partnerships, here’s a hard truth: you are only as compliant as your weakest partner.
Every time you plug into a crypto provider for liquidity, exchange, or settlement, you're tying your business reputation to theirs. If their KYC (Know Your Customer) process is weak, incomplete, or non-compliant, you inherit that risk. That means exposure to:
- Regulatory sanctions
- Frozen user accounts
- Delays in onboarding or payouts
- Loss of user trust
At Obiex, we treat compliance as core infrastructure, not a checkbox. This guide helps you evaluate whether your crypto partner does the same.
What Is a Crypto Partner’s KYC Stack?
When we talk about a crypto partner’s KYC stack, we’re referring to the entire system they use to identify, verify, and monitor their users for compliance and risk purposes.
This stack is made up of tools, processes, third-party services (vendors), internal policies, and storage systems that work together to meet KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (Anti-Money Laundering) requirements.
Simply put, a KYC stack is how a crypto company checks that its users are legit, not fraudsters or sanctioned individuals, and how it keeps that information safe and updated.
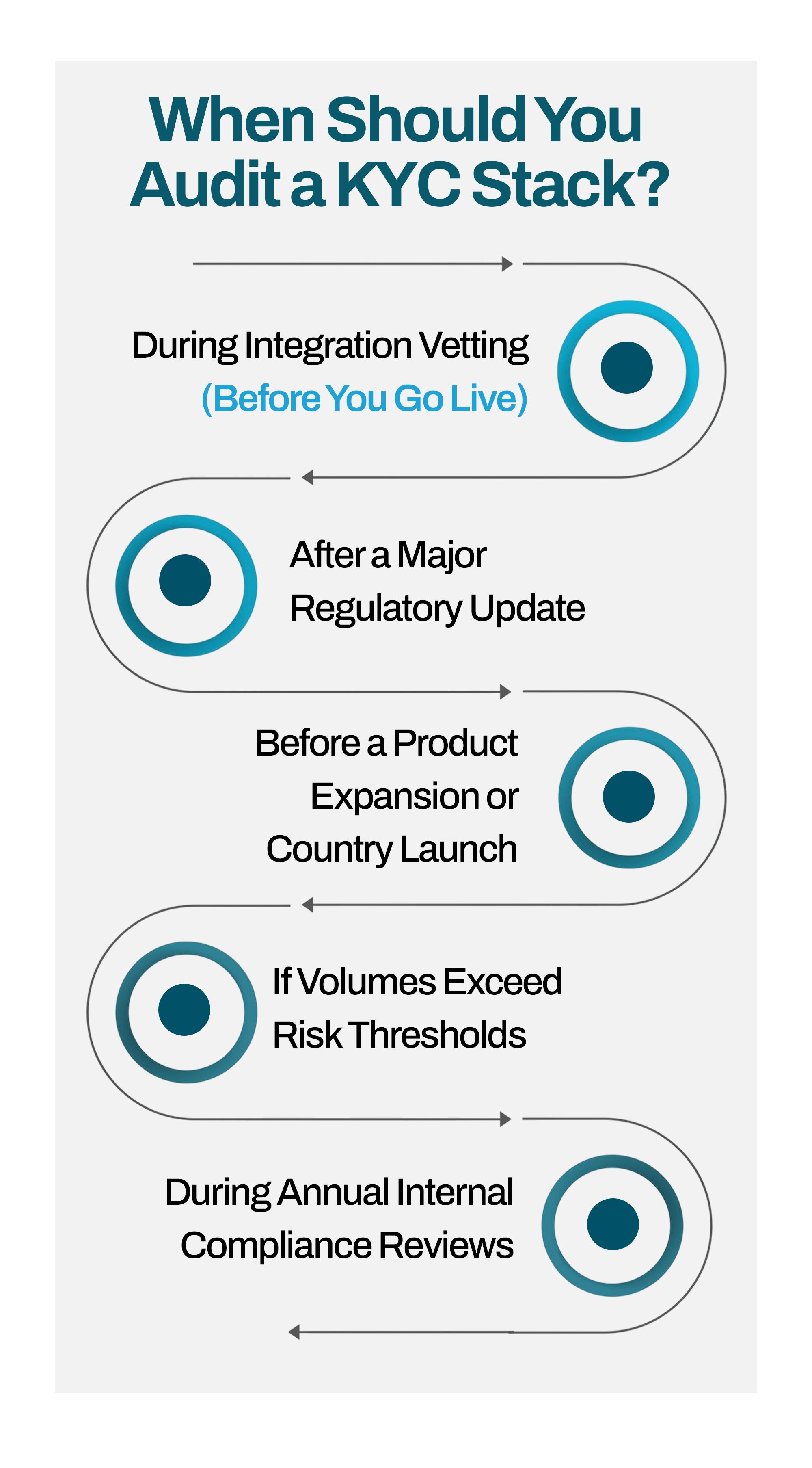
When Should You Audit a KYC Stack?
Auditing your crypto partner’s KYC stack isn’t just a one-time task. It’s a critical part of ongoing due diligence, especially when your platform relies on another company’s systems to verify users and stay compliant.
If something goes wrong in their KYC process, it becomes your problem too. That’s why knowing when to audit is just as important as knowing how to audit.
You should audit a KYC stack:
1. During Integration Vetting (Before You Go Live):
Before you sign any agreement or go live with a crypto partner’s API, you need to review their entire KYC infrastructure. That includes the tools they use, the vendors they rely on, the data they store, and the way they screen and monitor users.
What to look for:
- Documented KYC/AML policy
- List of KYC tools and vendors
- Real examples of KYC flows
- Demo of user onboarding process
- SLA terms for risk escalations
2. After a Major Regulatory Update:
Laws and compliance standards change frequently, especially in crypto.
If your partner hasn’t adapted their KYC process after a regulatory update, your platform could fall out of compliance without realising it.
Tip: Keep a checklist of compliance changes in your operating regions and ask your partner how they’ve responded to each one.
3. Before a Product Expansion or Country Launch:
Are you expanding into a new country or launching a high-risk product like crypto trading or P2P remittances?That’s the time to re-audit your partner’s KYC stack.
Each market has its own KYC rules. What is acceptable in Kenya may not meet the requirements in the EU or Ghana.
4. If Volumes Exceed Risk Thresholds:
As your platform grows, the risk exposure increases. If you go from 1,000 to 50,000 users, or handle millions in monthly volume, a minor KYC flaw can become a major liability.
This is where many platforms get blindsided; by assuming the system that worked at small scale will hold up at scale.
If your user base or transaction volume has grown significantly, it’s time to reassess your partner’s controls.
5. During Annual Internal Compliance Reviews:
Whether required by your investors, board, or regulators, an annual audit of your third-party KYC infrastructure should be a standard part of your risk management process.
This gives your internal compliance team a chance to:
- Confirm that your crypto partner is still following current standards
- Ensure that any past issues have been resolved
- Document the partner’s compliance status for future audits or fundraising rounds
What You Need Before Auditing
1. Access to Vendor List and Documentation:
Start by asking your partner for a complete list of their KYC and AML vendors. This should include:
- The names of each vendor (e.g., Sumsub, Jumio, Ondato)
- The specific services each one handles (IDV, PEP screening, liveness, etc.)
- The countries or regions they cover
- Any certifications or licenses they hold (e.g., ISO 27001, SOC 2, GDPR, NDPR)
Also request:
- Process documentation (onboarding flowcharts, risk rules)
- Sample compliance reports or exportable audit logs
- Their KYC/AML policy documents
If your partner can’t provide this, that’s already a red flag.
2. Regulatory Alignment Checklists:
You need to clearly understand the compliance requirements in the markets where you operate or plan to operate.
This includes rules from:
- National regulators (e.g., CBN, CMA, FSCA, SEC)
- International bodies (e.g., FATF, OFAC, EU AML directives)
- Data protection laws (e.g., Nigeria’s NDPR, Kenya’s Data Protection Act, GDPR)
Create a checklist of must-haves per region. Then compare it against what your crypto partner’s KYC stack actually supports.
Example:If you’re launching in Ghana, your checklist might require biometric ID support (Ghana Card), local document recognition, and cross-border risk screening. Your partner’s stack needs to reflect that.
3. An Internal or External Compliance Specialist:
If you don’t have an in-house compliance lead, bring in a qualified consultant to help you assess:
- The quality of the partner’s onboarding process
- Their sanctions monitoring setup
- Whether their risk models are fit for your use case
- How well they manage data security and vendor oversight
This is especially important for high-risk use cases, such as remittance platforms, crypto-to-fiat swaps, or B2B settlements.
4. Understanding Your Own Compliance Obligations:
Before you audit someone else’s system, make sure you fully understand what you’re responsible for under the law.
Even if your crypto partner is handling KYC, you still carry the regulatory burden as the platform owner or operator.
Ask yourself:
- Are you required to collect and store KYC data?
- Do regulators in your region allow third-party KYC delegation?
- Are there KYC thresholds (e.g., per transaction or per day) that trigger enhanced checks?
- Do you need to report suspicious transactions or maintain internal records?

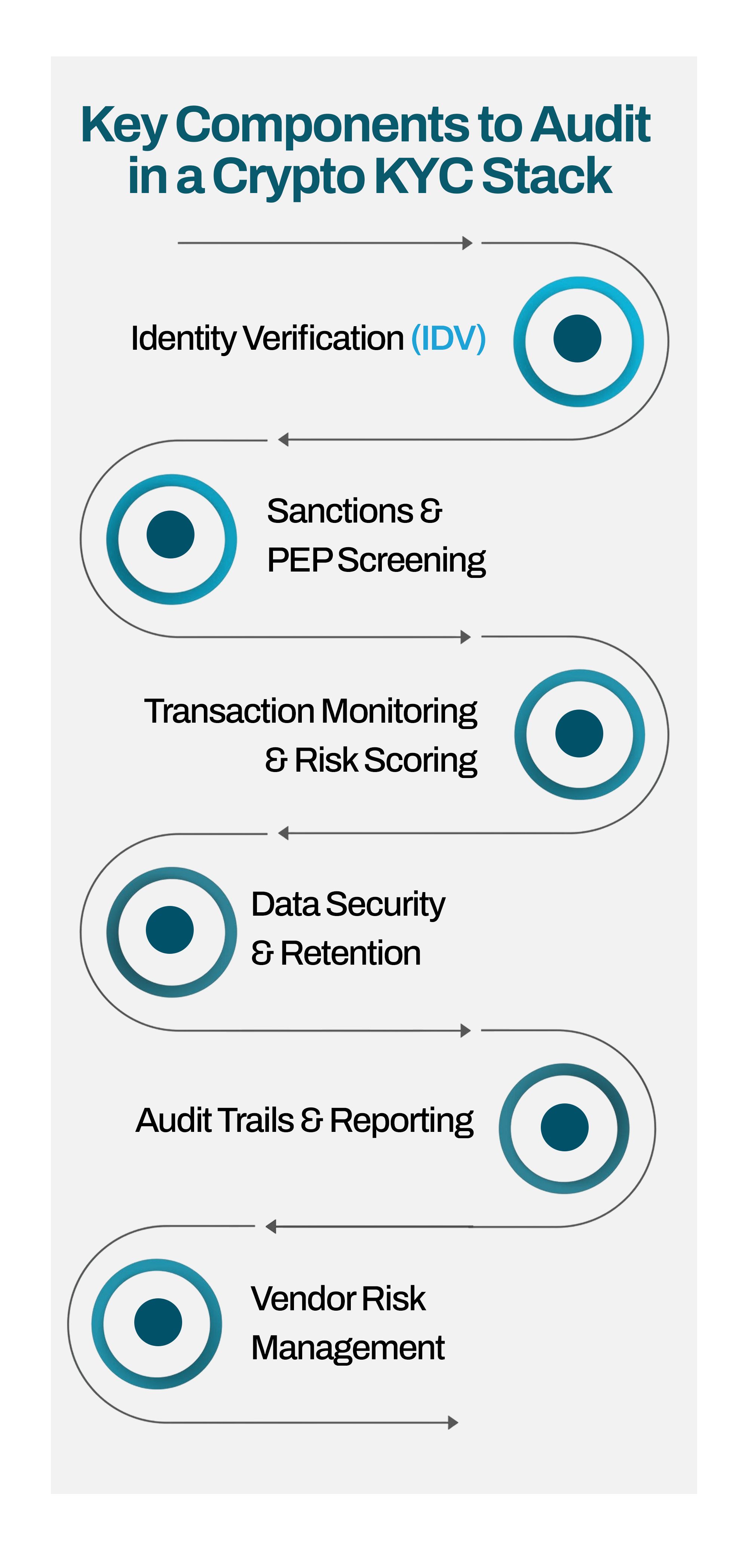
Key Components to Audit in a Crypto KYC Stack
1. Identity Verification (IDV):
This is the first and most visible layer of KYC. It involves collecting and verifying personal information and documents from users during onboarding.
What to Check:
- Is the ID verification process automated, manual, or hybrid?
- Does it include document verification, selfie checks, and liveness detection?
- Can it handle users from your target regions (e.g., West, East, and Southern Africa)?
- How long does it take to complete the KYC process?
- Are fraud checks applied during verification?
Red Flags:
- Manual KYC only (too slow and error-prone)
- No liveness detection (risk of identity theft or spoofing)
- Inability to process local IDs (e.g., Ghana Card, NIN, PVC)
- Long KYC turnaround times (delays in user activation)
2. Sanctions & PEP Screening:
Sanctions screening ensures that users aren’t flagged by international authorities. PEP (Politically Exposed Person) screening identifies users who may pose a higher risk.
What to Check:
- Are sanctions and PEP lists checked at onboarding and on an ongoing basis?
- What data sources are used (e.g., OFAC, UN, EU, FATF)?
- How frequently are these sources updated?
- Can the partner demonstrate how flagged users are handled/escalated?
Red Flags:
- Only one-time checks at onboarding (no real-time monitoring)
- Outdated or incomplete data sources
- No clarity on escalation timelines for flagged users
- No documentation of action taken on past alerts
3. Transaction Monitoring & Risk Scoring:
This monitors user behaviour after onboarding and flags unusual or risky activity, such as rapid transfers, account layering, or large volume shifts.
What to Check:
- Is there real-time transaction monitoring in place?
- Are there risk models or tiering logic applied to user accounts?
- Are alerts automated or handled manually?
- Are actions (e.g., freezing, investigation) logged and reportable?
Red Flags:
- No behavioural analysis beyond basic volume checks
- Risk scoring applied manually or inconsistently
- No automatic alert system for unusual activity
- Lack of logs or audit trails for escalated transactions
4. Data Security & Retention:
Compliance isn’t just about checks. It’s about how the data is stored, encrypted, and retained over time.
What to Check:
- Where is the data stored? (locally, regionally, or offshore?)
- What encryption protocols are used (e.g., AES-256, SSL)?
- How long is user data retained?
- Are data access logs kept and reviewed regularly?
- Is the infrastructure compliant with NDPR, GDPR, or other relevant data laws?
Red Flags:
- Data stored in jurisdictions with weak data protection laws
- No mention of encryption standards
- Retention periods not aligned with regional laws
- No access control system or record of who accessed KYC data
5. Audit Trails & Reporting:
Your ability to trace historical activity and present clean reports to regulators depends on the quality of your partner’s audit logs and compliance reporting tools.
What to Check:
- Can audit logs be exported on demand (e.g., for onboarding, escalations, transactions)?
- What format are reports provided in? (PDF, CSV, dashboard view?)
- Are compliance events timestamped and user-linked?
- How quickly can reports be generated for regulatory review?
Red Flags:
- No exportable audit trail
- Limited or static reporting formats
- Incomplete history of compliance decisions
- No visibility into resolved or unresolved KYC cases
6. Vendor Risk Management:
Most crypto platforms use third-party vendors to handle some parts of their KYC process. You need to assess not just the partner, but also who your partner relies on.
What to Check:
- Who are the actual KYC vendors? (e.g., Sumsub, Jumio, Ondato)
- Are vendors licensed and certified?
- Are there SLAs (Service Level Agreements) for performance, downtime, and issue resolution?
- How often does your partner review and assess these vendors?
Red Flags:
- Unknown or unregulated KYC vendors
- No SLA for user onboarding or flagged cases
- Over-reliance on a single tool or vendor without backup
- No documented process for vendor evaluation or rotation
Questions You Should Ask Your Crypto Partner (Checklist)
Use this checklist during your crypto partner evaluation or integration planning process:
KYC Stack & Process
- What risk scoring or tiering system do you use for users?
- Do you conduct ongoing monitoring, or just onboarding?
- Do you screen users against sanctions and PEP lists?
- Do you perform liveness detection and selfie checks?
- Do you support ID verification for our target countries?
- Is your identity verification process automated, manual, or both?
- What KYC tools and vendors do you use?
Data Security & Compliance
- Can you provide exportable audit trails and compliance reports on demand?
- Who has access to stored KYC information?
- How long do you retain KYC data?
- How is user data encrypted?
- Where is user data stored?
Escalation & Vendor Oversight
- Do you provide ongoing compliance support after integration?
- Can we test the KYC flow before going live?
- Have you passed any recent audits or compliance assessments?
- Are your KYC vendors licensed and regularly reviewed?
- How quickly do you respond to flagged or high-risk users?
Red Flags to Watch Out For
- No clear documentation of their KYC/AML process
- Inability to name or disclose third-party KYC vendors
- The KYC process is fully manual with no automation
- No real-time sanctions or PEP screening in place
- Missing or outdated data encryption and storage policies
- No SLA for responding to suspicious or high-risk activity
- Incomplete or unavailable audit trails and compliance reports
- Vendors are unlicensed, unregulated, or rarely reviewed
- No system for ongoing user risk monitoring
- One-size-fits-all onboarding without country-specific rules
- No dedicated compliance contact or support channel
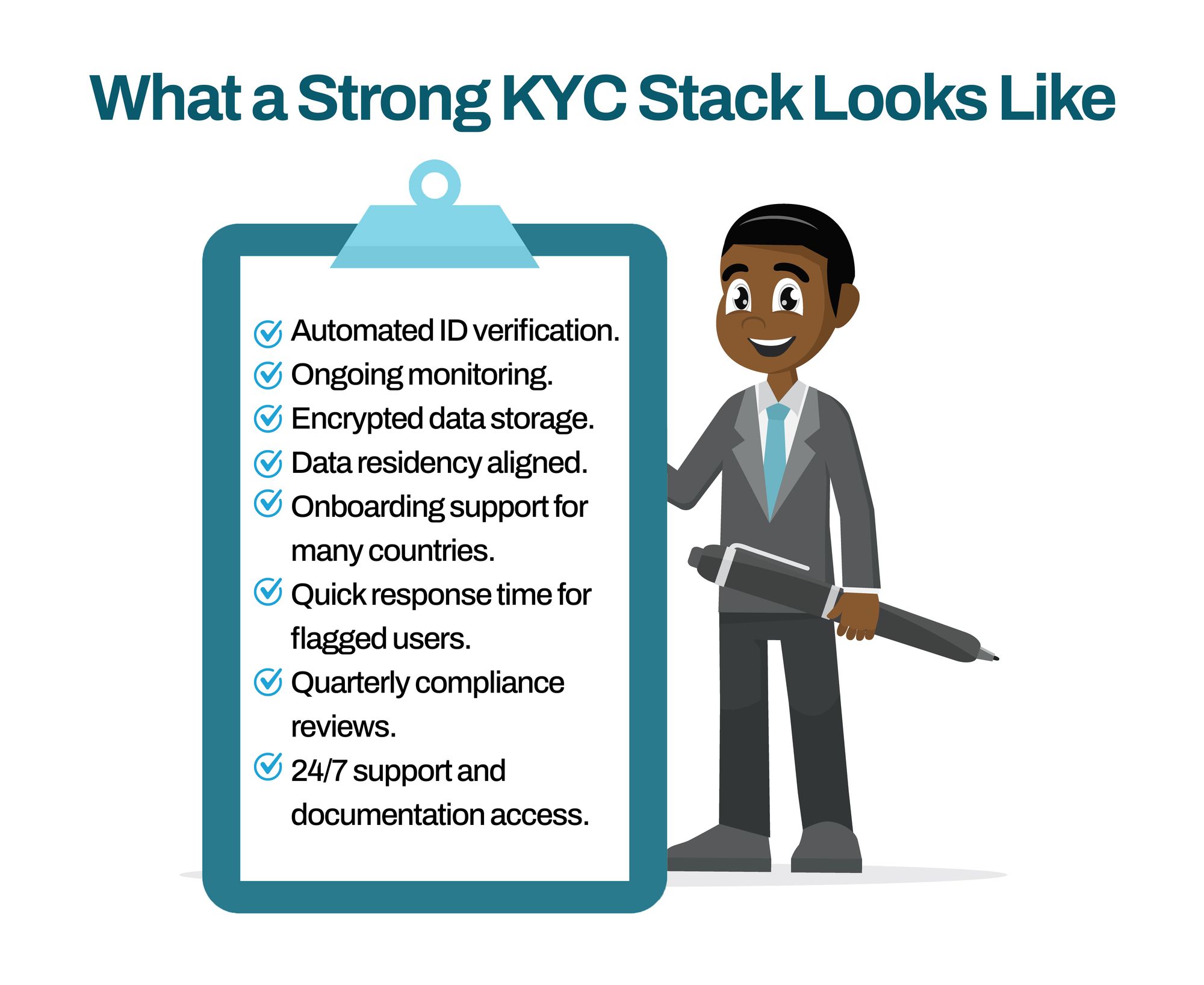
What a Strong KYC Stack Looks Like (Obiex’s Approach)
A strong KYC stack should be fast, compliant, scalable, and built to adapt across regions. Here’s what that looks like at Obiex:
- Automated ID verification with support for local and international ID types
- Ongoing monitoring for high-risk behaviour and unusual transaction patterns
- Encrypted data storage using AES-256 and SSL standards
- Data residency aligned with NDPR, GDPR, and other regional laws
- Onboarding support for many countries
- Quick response time for flagged users with internal escalation flow
- Quarterly compliance reviews to stay ahead of regulation changes
- 24/7 support and documentation access for internal and external audits
How Obiex Helps You Integrate with Confidence
Obiex was designed to support fast-moving financial platforms with enterprise-grade infrastructure and end-to-end KYC compliance built in.
Here’s how we help you integrate with confidence:
- Battle-Tested Compliance Framework:Obiex is built with layered KYC, AML, and transaction monitoring from the ground up, ready for local and international audits.
- Pre-Integrated KYC Tools:Our APIs come bundled with real-time ID verification, sanctions screening, and risk flagging. So you don’t have to set these up separately.
- Enterprise-Grade Crypto Liquidity:Get access to compliant, high-volume liquidity and settlements, whether you’re building a wallet, FX product, or trading platform.
- Fast-Track API Integration:With well-documented endpoints and sandbox environments, your team can go live in days, not weeks.
- Built for African and Global Volumes:Obiex supports KYC and onboarding for many countries, including Nigeria, Ghana, and Cameroon.
- Ongoing Compliance Support:We provide full compliance walkthroughs, quarterly KYC reviews, and immediate access to documentation and reports.
- 24/7 Onboarding & Technical Assistance:Our support team works closely with your compliance, product, and engineering teams to resolve blockers fast.
- Scalable Infrastructure:Whether you’re onboarding 500 users a month or 100,000, Obiex scales with you, securely and reliably.
To Recap
KYC is a core part of your business infrastructure. If your crypto partner’s KYC stack is weak, your whole operation is at risk.
The good news is that auditing doesn’t need to be complicated. It just needs to be thorough.
👉 Are you looking for a crypto partner with comprehensive compliance measures?Join the thousands of fintechs using Obiex for secure, fast, and compliant crypto integrations.
FAQs
Q1. What is a KYC stack in crypto?
A KYC stack is the full set of tools and processes a crypto platform uses to verify users, screen for fraud, and stay compliant with regulations.
Q2. Why do I need to audit my crypto partner’s KYC stack?
Weak KYC processes can expose you to fines, user account issues, or loss of licensing.
Q3. What tools should be in a strong KYC stack?
Identity verification (IDV), sanctions screening, transaction monitoring, risk scoring, and audit-ready reporting.
Q4. How do I know if a KYC vendor is reliable?
Check if they are regulated, provide clear SLAs, and are used by other credible fintechs.
Q5. How long does Obiex take to onboard a user?
Under 2 minutes for most users, using automated KYC tools.
Q6. Is Obiex compliant in Africa?
Yes, Obiex supports regulatory standards across Nigeria, Ghana, Cameroon, and more.
Q7. Can I customise KYC thresholds on Obiex?
Yes, you can adjust based on your product and risk appetite.
Q8. Does Obiex support real-time sanctions checks?
Yes, Obiex uses ongoing screening with updated global data.
Q9. What happens if a user is flagged?
Escalation happens within 30 minutes through internal compliance channels.
Q10. Is KYC included in Obiex APIs?
Yes. Obiex crypto APIs include KYC and AML capabilities as part of the integration stack.
Disclaimer: This article was written to provide guidance and understanding. It is not an exhaustive article and should not be taken as financial advice. Obiex will not be held liable for your investment decisions.