Table of Contents
- What Is a Centralised Exchange?
- What Is a Decentralised Exchange?
- CEX vs DEX: Pros & Cons Breakdown
- Comparison Table: CEX | DEX | Obiex
- When to Use a CEX
- When to Use a DEX
- To Recap
- FAQs
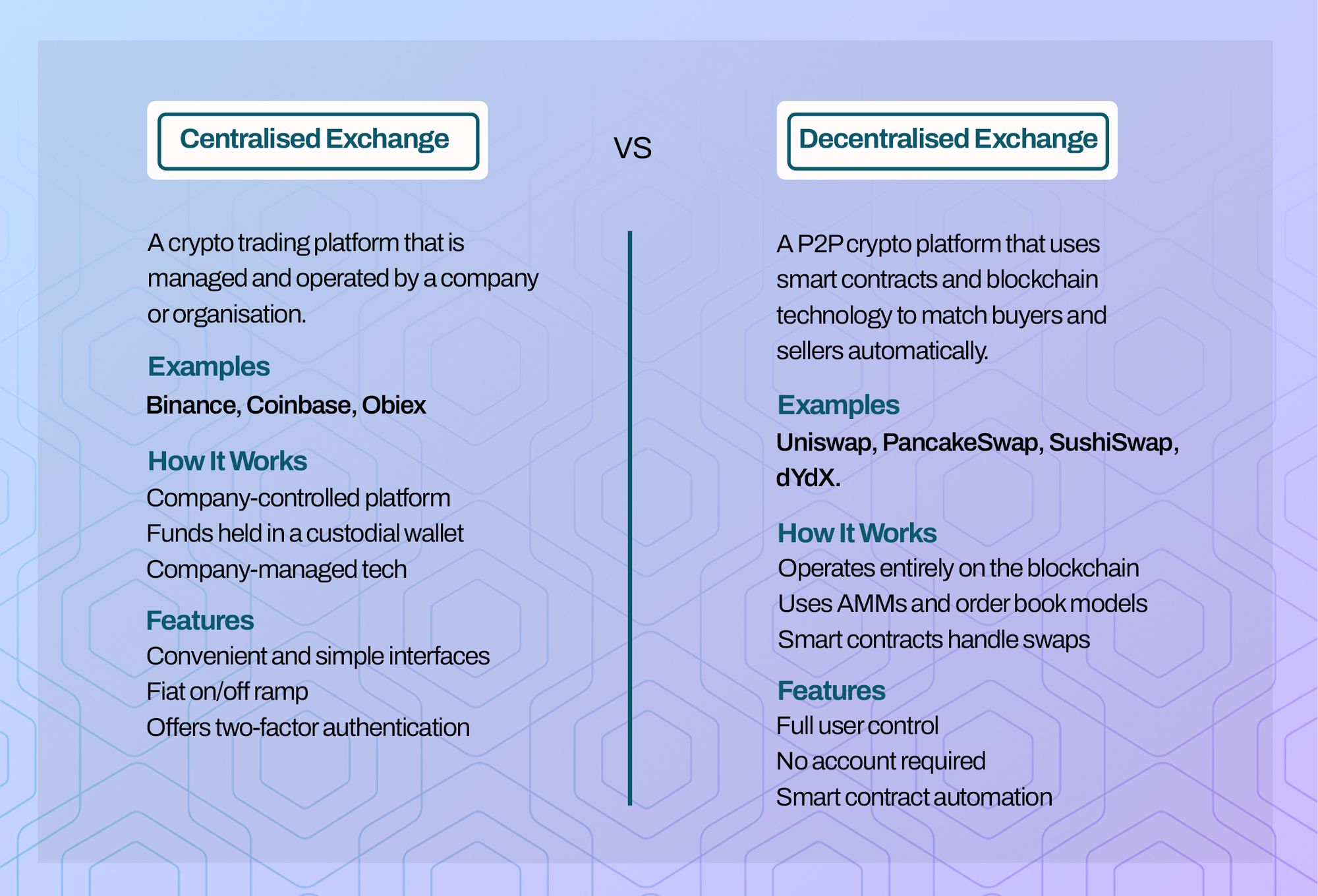
What Is a Centralised Exchange?
A centralised exchange (CEX) is a crypto trading platform that is managed and operated by a company or organisation.
Think of it like a traditional bank for crypto (but better).
Examples:
Popular examples of these include companies like:
- Binance
- Coinbase
- Obiex
How It Works:
- On a centralised exchange, the company controls the platform, holds the users' funds in what is called a custodial wallet, and manages all the technical stuff behind the scenes.
- This setup makes it very easy for new and intermediate users to get started because you don’t need to worry about handling complicated blockchain addresses, private keys, or self-custody risks.
- You simply sign up, complete basic identity verification (known as KYC), deposit your funds, and start trading.
Key Features:
- One of the biggest advantages of centralised exchanges is convenience and user experience (UX).
- They offer simple interfaces, mobile apps, instant swaps, and responsive customer support if anything goes wrong.
- Centralised exchanges also make it much easier to move money between your local bank and your crypto wallet. This is referred to as a fiat on/off ramp.
- Centralised exchanges are also more attractive to security-conscious users, since most of them offer features like two-factor authentication (2FA), insurance for stored funds, and regulatory compliance.
- However, because they are controlled by companies, users must trust that the platform is secure, well-managed, and not vulnerable to hacks or regulatory shutdowns.
What Is a Decentralised Exchange?
A decentralised exchange is a peer-to-peer (P2P) crypto platform that uses smart contracts and blockchain technology to match buyers and sellers automatically.
On a DEX, you stay in full control of your crypto because you trade directly from your own wallet. The exchange doesn’t hold your funds.
This means your private keys (which control access to your crypto) remain with you at all times.
You simply connect your wallet to the DEX, place your trade, and the smart contract handles the rest.
How It Works:
DEXs operate entirely on the blockchain, using automated market makers (AMMs) or order book models.
In the AMM model (which is more common today), users provide liquidity to trading pools, and trades happen based on algorithms that calculate prices.
For example, if you want to trade USDT for ETH, you swap directly with the liquidity pool, rather than with another trader.
All transactions occur directly on-chain, which provides more transparency but also results in higher gas fees, depending on the blockchain network (Ethereum gas fees can sometimes reach $20–50 per transaction during congestion).
This process can be summarised into the following steps:
- You connect your wallet (e.g. MetaMask, Trust Wallet).
- You trade directly from your wallet.
- Smart contracts automatically handle the swap.
Examples:
Some of the most popular decentralised exchanges include:
- Uniswap (Ethereum-based)
- PancakeSwap (Binance Smart Chain-based)
- SushiSwap (multi-chain)
- dYdX (focused on decentralised derivatives)
These platforms handle billions of dollars in trading every month, and they operate 24/7 without downtime.
Key Features:
- Full User Control: You control your keys, funds, and trades at all times.
- No Account Required: You don’t need to register or verify your identity (no KYC).
- Smart Contract Automation: Trades are executed automatically based on preset rules.
- Transparency: All trades are publicly recorded on the blockchain.
- Higher Risks: You are responsible for your wallet security. If you lose your keys, your crypto is gone.
- Variable Fees: Gas fees can be high, especially on popular blockchains like Ethereum. However, some chains like BSC and Solana offer cheaper alternatives.
- Limited Customer Support: Unlike centralised platforms, DEXs don’t have human support teams if you encounter issues.
CEX vs DEX: Pros & Cons Breakdown
Now let’s do a side-by-side comparison to better understand the differences between CEX and DEX.
1. Security: CEX is safer for beginners; DEX is safer if you know what you're doing
Security is usually the first thing people care about.
With centralised exchanges (CEX) like Obiex, Binance, or Coinbase, your crypto is stored by the platform. This means you don’t have to worry about managing complicated wallets, private keys, or seed phrases. If you forget your password, our customer support team can assist you in recovering your account funds. This makes CEX platforms generally safer for beginners or for users who prioritise ease.
On the other hand, decentralised exchanges (DEX) don't store your funds or keys. You hold your crypto in your own private wallet, like MetaMask or Trust Wallet. This gives you full control, but also full responsibility. If you lose your keys or make a mistake in a transaction, there is no customer support to assist you. While DEX offers control, the risks are much higher if you’re not careful.
2. Fees: CEX Fees vs DEX Gas Fees
When it comes to fees, centralised exchanges (CEXs) and decentralised exchanges (DEXs) operate quite differently.
DEXs often require users to pay gas fees. The cost of gas fees can vary widely depending on network activity. For instance, swapping tokens on popular DEXs may cost anywhere from $5 to $50 or more, especially during periods of high demand on networks like Ethereum. This means that even small trades, such as a $100 swap, might incur significant fees.
Centralised exchanges, on the other hand, typically do not charge gas fees since transactions occur off-chain within the platform's internal system. Instead, they may charge trading fees, which are usually a small percentage of the transaction amount. Some CEXs also offer fee-free swaps for certain trading pairs, allowing users to exchange assets without additional costs related to network congestion or fluctuating gas prices.
3. Liquidity: CEX usually wins (most of the time)
Liquidity simply refers to how easily you can buy or sell your crypto at a good price.
Centralised exchanges generally have more liquidity because they pool orders from thousands (or millions) of users. Binance, for instance, achieves daily trading volumes exceeding $10 billion. Obiex, though smaller, provides users with tight spreads.
DEXs, often have lower liquidity, especially for less popular tokens. This can result in price slippage, where you end up paying more (or receiving less) than expected.
Verdict: If you’re swapping stablecoins or popular tokens, DEXs may be suitable. But for high-volume trading, CEX liquidity is often more reliable.
4. Speed & Convenience: CEX= instant swaps, DEX = longer wait
Speed matters, especially in crypto, where prices fluctuate rapidly and constantly.
CEXs typically offer instant swaps, user-friendly apps, access to fiat currencies, and customer support. Trades are processed off-chain, so users don’t have to wait for blockchain confirmations or deal with failed transactions.
On most DEXs, your swap depends on blockchain confirmation times. Ethereum takes about 15 seconds to a few minutes per transaction, but during high traffic, delays can stretch longer. And if gas prices spike, you either wait or pay more.
5. Control: DEX gives full control, but also full risk
One major selling point of DEXs is the control they offer. You own your private keys, your crypto stays in your wallet, and no one can freeze your funds. This aligns with the DeFi principle: "Not your keys, not your coins." However, this control comes with full risk. One mistake (wrong wallet address, phishing attack, lost seed phrase) and your funds are gone permanently.
CEXs, while holding your funds in custody, add layers of protection: encrypted storage, multi-factor authentication, customer support, and insurance in some cases. For many African traders who want security, convenience, and speed, this is a safer and more practical option.
Comparison Table: CEX | DEX | Obiex
When to Use a CEX
1. You Want to Swap USDT to NGN, GHS, or XAF:
If you’re trading crypto in Nigeria, Ghana, or Cameroon, one of the biggest challenges is converting your crypto into local currency like Naira (NGN), Cedi (GHS), or Central African CFA Franc (XAF).
Most decentralised exchanges don’t support fiat currencies directly. On a DEX, you can swap tokens, but you can’t easily withdraw to your local bank account.
A CEX like Obiex allows you to directly convert your USDT or Bitcoin into Naira, Cedi, or CFA and withdraw the funds to your bank account, usually within minutes.
2. You Need Fast Support and Fiat Withdrawal:
Centralised exchanges offer customer support you can contact when something goes wrong. This is something you won’t get with most DEX platforms.
For example, if a transaction fails or you experience certain challenges, Obiex customer support can sometimes assist or at least guide you.
On DEX platforms, there is no customer service. Your funds are lost if an error occurs.
Also, fiat withdrawals are much faster on CEX platforms. On Obiex, for instance, you can withdraw NGN, GHS, or XAF to your bank in real-time or within a few hours, depending on the method you use.
3. You’re Doing High-Volume Trading:
If you're a business, OTC desk, or high-volume trader, CEX platforms typically handle large trades more efficiently than DEX platforms.
On decentralised exchanges, large trades often suffer from price slippage, meaning the price moves while your trade is being processed.
On a CEX, the order book system can fill large orders with much less slippage, giving you better pricing for bulk transactions.
4. You Want to Avoid Gas Fees:
Decentralised exchanges often run on blockchains like Ethereum, where gas fees can get very high, especially during network congestion.
Even on cheaper chains like Binance Smart Chain, fees can add up if you trade frequently.
Centralised exchanges like Obiex don’t charge blockchain gas fees for swaps or trades because transactions happen within their internal system.
This makes CEX platforms cheaper for regular traders, small businesses, and high-volume traders who want to swap crypto without gas fees eating into their profits.

When to Use a DEX
1. You’re Deep in DeFi / Altcoin Land:
If you're trading smaller or newer coins that haven’t made it to big centralised platforms like Binance or Obiex, you’ll likely find them on a DEX.
DEXs give you access to early-stage tokens and DeFi projects that aren’t yet widely available.
For example, Uniswap on Ethereum or PancakeSwap on BNB Smart Chain often list new tokens within days or even hours of launch.
This makes DEXs valuable for high-risk, high-reward trading, but you have to be careful of scams and rug pulls, which are more common in these early-stage tokens.
2. You Prefer Full Wallet Custody:
With DEXs, you hold your own keys and control your funds at all times. This is called self-custody.
Unlike CEXs where your funds are held by the platform, on a DEX your crypto stays in your personal wallet (like MetaMask or Trust Wallet) until you make a trade.
For some traders, especially after the collapse of centralised platforms like FTX, this extra control feels safer.
However, self-custody also means you’re 100% responsible for your wallet security. If you lose your private keys, there’s no customer service to help recover your funds.
3. You’re Exploring Tokens Not Listed on Major Exchanges:
Many smaller or experimental projects don't meet the strict listing rules of major centralised exchanges.
A DEX allows you to trade these tokens directly from your wallet using liquidity pools provided by other users.
For example, if you're interested in a niche DeFi lending token or a gaming token that’s gaining popularity in African markets, you’ll often find it on a DEX before it appears on CEXs.
4. You’re OK with Paying Gas and Figuring Things Out Yourself:
Trading on a DEX typically involves paying network gas fees, which can vary significantly.
On cheaper chains like Arbitrum, BNB Chain, or Solana, fees can be as low as a few cents.
Also, DEXs usually don’t offer customer support, fiat on-ramps, or simple trading interfaces.
You’ll need to know how to connect your wallet, manage slippage, avoid scam tokens, and handle failed transactions.
If you’re comfortable with these technical steps, a DEX can offer powerful flexibility that CEXs don’t.
To Recap
At the end of the day, both centralised and decentralised exchange platforms have their strengths.
- CEXs offer security, support, and convenience.
- DEXs offer freedom, variety, and control.
But smart traders know they don’t have to pick one or the other. That’s where Obiex comes in, because it gives African traders a hybrid model that combines the best of both worlds:
- Zero-fee swaps
- Fast fiat withdrawals (NGN, GHS, XAF)
- Security with excellent customer support
- Smooth user experience
👉No more choosing between safety and freedom. With Obiex, you get both.
Sign up now to swap, send, trade, and withdraw in your local currency, faster, safer, and gas-free.
FAQs
Q1. What is the main difference between CEX and DEX?
CEX is managed by a company (e.g. Obiex, Binance), while DEX uses smart contracts with no middleman (e.g. Uniswap).
Q2. Which crypto exchange is better for beginners?
A centralised exchange like Obiex is better for beginners due to its security, support, and easy-to-use interface.
Q3. Are DEXs safer than CEXs?
They are safer only if you fully understand crypto security. Otherwise, CEX platforms offer stronger protection for everyday users.
Q4. Can I trade fiat currencies on a DEX?
Usually no. DEXs rarely support fiat currencies like NGN, GHS, or XAF. That’s where CEX platforms shine.
Q5. How do gas fees affect my trading?
On DEXs, gas fees can eat into your profits, especially on Ethereum. Obiex Swap eliminates these gas fees entirely.
Q6. Which is faster: CEX or DEX?
CEX is usually faster due to centralised servers. DEX speed depends on blockchain congestion.
Q7. Do I need to verify my ID on a CEX?
Yes, most CEX platforms require KYC (Know Your Customer) verification for compliance and security.
Q8. Can I access DeFi tokens on Obiex?
Obiex focuses on major cryptocurrencies but lets you swap crypto without gas fees easily. For exotic tokens, you may need a DEX.
Q9. How do I avoid high fees when trading crypto?
Use platforms like Obiex to trade crypto securely with zero-fee swaps and avoid costly blockchain gas fees.
Q10. Is Obiex available in Nigeria, Ghana, and Cameroon?
Yes. Obiex offers localised solutions for African users to trade crypto in Nigeria securely, as well as in Ghana and Cameroon.
Disclaimer: This article was written to provide guidance and understanding. It is not an exhaustive article and should not be taken as financial advice. Obiex will not be held liable for your investment decisions.



